In the modern healthcare industry, patient experience has emerged as the cornerstone of quality care. As patients become more informed and empowered, they no longer act as passive recipients of services. Instead, they demand care that is tailored and seamless. This shift leads healthcare organizations to adopt patient-centered models. This holistic approach focuses on the whole patient experience instead of just the treatment.
Research indicates that organizations focusing on patient experience achieve better health outcomes, reduced readmission rates, and improved patient loyalty. For instance, a Press Ganey Report found that hospitals with higher patient experience scores had 15% lower readmission rates. Additionally, a Deloitte study revealed that 92% of patients would prefer a hospital that offers personalized care. These findings underscore the importance of enhancing patient experience as a means to build loyalty, improve satisfaction, and achieve better clinical outcomes.
As competition gets tougher, patient experience becomes a key differentiator. It affects reputation, patient retention, and operational efficiency. Healthcare providers who invest in improving this area will be successful in an environment where patient satisfaction and loyalty are tied to organizational performance.
Improving patient experience extends beyond mere satisfaction. It significantly influences health outcomes and operational efficiency. Studies show that patients who feel supported by their healthcare providers are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and attend follow-up appointments. This engagement is essential, as patient-centered care models are linked to improved chronic disease management and reduced hospitalization rates.
Also, improving patient experience has a positive effect on financial performance. Research shows that hospitals with strong patient experience metrics not only achieve better clinical outcomes but also lower operational costs. This correlation shows that care is effective and that patients' experience is important in healthcare organizations.
In care models where providers are paid based on how well patients do and how satisfied they are, it's important to make sure patients have a good experience. Therefore, healthcare administrators and executives must create a supportive and engaging environment for patients, which will ultimately lead to healthcare success.
This article will explore key challenges and strategies healthcare organizations can use to improve patient experience. We also will look at ways to use technology to give better care and make communication and operations better. This will help healthcare providers give quality care and foster long-term patient loyalty.
This comprehensive guide will help healthcare managers, care coordinators, and executives create a more patient-centered healthcare environment that delivers both quality care and positive outcomes.
Understanding Patient Experience in Healthcare
Defining Patient Experience
Patient experience refers to the comprehensive sum of all interactions that patients have with the healthcare system. It encompasses every aspect, from initial appointment scheduling to post-treatment care. It is a multifaceted concept. Reflecting the quality of medical treatment received, the emotional and psychological dimensions of care.
The ease of accessing services, the quality of communication with healthcare providers, the responsiveness of staff, and the environment in which care is delivered are critical components of the patient experience. Understanding and delivering patient experience is crucial for healthcare organizations. By meeting patient needs and expectations, healthcare organizations can improve satisfaction and foster positive outcomes.
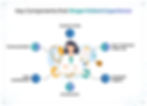
Here, several key touchpoints influence how patients perceive their healthcare experience:
Access to Care: A fundamental aspect of patient experience that influences how quickly and effectively patients can receive medical attention. The ability to schedule appointments easily, receive timely care, and navigate the healthcare system is crucial. Barriers such as long wait times, complex administrative processes, or difficulty accessing services can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction.
Communication: Effective communication is pivotal in shaping patient experience. Along with the clarity of information provided, the empathetic manner in which it is delivered is important, too. Compassionate communication between healthcare providers and patients builds trust. Effective communication involves active listening, allowing patients to express their concerns, and providing clear explanations about diagnoses, treatment options, and care plans. When patients feel heard and understood, their trust in healthcare providers increases, promoting adherence to treatment and engagement in their care.
Care Coordination: The coordination of care among various healthcare providers plays a vital role in ensuring a seamless experience, especially for patients with complex health conditions requiring input from multiple specialists. Poor coordination can lead to fragmented care, resulting in confusion, miscommunication, and potential health risks. Effective care coordination involves establishing clear communication channels among providers and ensuring that all team members are informed about the patient's medical history, preferences, and ongoing treatments. Patients experience smoother transitions and a more integrated approach to their health, which can lead to better outcomes.
Environment: The physical environment of healthcare facilities greatly impacts patient perceptions and comfort levels. A clean, organized, and welcoming atmosphere can reduce anxiety and make patients feel valued. A chaotic or uncomfortable setting may negatively impact how patients perceive their care. Factors such as comfortable waiting areas, accessible facilities, and the overall aesthetic contribute to the healthcare setting. A disorganized or unwelcoming environment can lead to negative impressions of the quality of care.
Emotional Support: Healthcare often involves navigating significant emotional challenges. Patients often face emotional stress alongside their medical challenges during serious illnesses or chronic conditions. Providing emotional support is crucial in enhancing patient experience. This can include compassionate care and patient education, and offering counseling, education, and emotional reassurance can significantly enhance patient well-being.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up: The healthcare experience does not end after treatment. Follow-up interactions, whether through phone calls or subsequent appointments, are critical to reinforcing the patient’s experience. These follow-ups provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to address any lingering concerns, assess the effectiveness of treatments, and gather feedback on the patient’s experience. A well-executed follow-up process can enhance patient satisfaction and strengthen the patient-provider relationship.
Impact on Clinical Outcomes and Patient Retention
Improving the patient experience is more than just getting higher satisfaction ratings. It directly affects clinical outcomes and patient retention. When patients have a good experience, they are more likely to follow their treatment plan, go back for check-ups, and take care of themselves. All this contributes to better health outcomes, such as improved chronic disease management and lower hospital readmission rates.
Also, a focus on patient experience can drive retention and loyalty. Happy patients are more likely to come back for more care and recommend providers to others. Negative experiences can be serious. Studies show that 16% of patients don't go back to the same provider after a bad experience, and 15% go to a different healthcare organization altogether (Consumer Perspectives on Patient Experience, 2024). Therefore, healthcare organizations that focus on patient experience can expect better clinical results and a more loyal patient base.
Common Challenges in Delivering Positive Patient Experiences
Despite the growing focus on patient-centered care and improving patient experience, healthcare organizations face several persistent challenges that hinder the delivery of high-quality care. These issues often lead to patient dissatisfaction and negatively impact clinical outcomes.

Below are key challenges that healthcare providers must navigate:
Long Wait Times: The primary source of patient dissatisfaction is extended wait time, which impacts both experience and health outcomes. The American College of Emergency Physicians says that 40% of patients are very upset because they have to wait a long time. Some even quit getting help because of the long wait. Waiting too long can make your health worse, especially when you need help right away. Also, research from the Journal of Emergency Medicine shows that patients who wait longer are 25% less likely to positively rate care experience.
Fragmented Care: When patients require treatment from multiple providers or specialities, their care can become fragmented, leading to miscommunication, duplicated tests, and disjointed follow-ups. Research from the National Institute of Health shows that 70% of patients feel their care is poorly coordinated. This lack of continuity can leave patients confused about their treatment plan, reduce adherence to recommendations, and increase the risk of medical errors.
Poor Communication: Ineffective communication between healthcare professionals and patients is a critical issue. When providers fail to clearly explain diagnoses, treatment options, or care instructions, patients may feel uninformed and distrustful. According to The Beryl Institute, 86% of patients say that clear communication is vital to their healthcare experience. Without proper dialogue, patients are more likely to misunderstand their conditions and treatment, leading to poor adherence and lower satisfaction. For instance, the World Health Organization estimates results in as much as a 50% drop in treatment effectiveness for chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Complex Administrative Processes: Healthcare often involves navigating complex administrative procedures. It starts from completing extensive paperwork to managing insurance claims. These paperwork problems can be frustrating, especially for older or chronically ill patients who often have to deal with the healthcare system. A Kaiser Family Foundation study found that 36% of patients have trouble with administrative tasks in healthcare. This can cause delays in care because of pre-authorization requirements and long forms to fill out. This complexity can make patients feel that administrative barriers overshadow the quality of care they receive.
Inconsistent Emotional Support: While clinical care is essential, many patients also require emotional support, especially when dealing with serious health conditions. However, healthcare settings do not always provide the necessary psychological support, leaving patients feeling anxious, isolated, or overlooked. A lack of empathy from staff can intensify these emotions, reducing patient trust and satisfaction. A study by the Cleveland Clinic found that 78% of patients felt that empathetic communication improved their overall experience, underscoring the value of compassion in care.
Impact on Patient Satisfaction and Care Outcomes
These challenges have serious repercussions for both patient satisfaction and health outcomes. Long wait times can discourage patients from seeking necessary care, leading to the progression of preventable conditions. Fragmented care often results in treatment delays, miscommunication, and unnecessary medical procedures, which can compromise patient safety. Poor communication undermines patient trust and can lead to non-compliance with treatment plans, further worsening health outcomes.
Addressing these challenges is essential for healthcare organizations aiming to improve patient experiences. By focusing on streamlining care coordination, reducing wait times, improving communication, and offering emotional support, providers can significantly enhance both patient experience and clinical results. It also contributes to overall public health.
Strategies to Improve Patient Experience
Creating a positive patient experience requires a multifaceted approach that meets patient needs, streamlines care delivery and builds trust in healthcare services.
Here are key strategies healthcare organizations can adopt to elevate the patient experience.

1. Personalized Care
Offering personalized care is fundamental to improving patient experiences. By tailoring care plans based on a patient's unique medical history, preferences, and cultural values, providers foster trust and engagement throughout the care experience. Research from the Journal of Patient Experience found that personalized care can improve patient outcomes by up to 30%, boosting trust and satisfaction.
Tailored Treatment Plans: Customized care ensures treatment is relevant and responsive to individual needs. This can include lifestyle-focused interventions, personalized medication plans, or alternative treatments that align with specific health requirements. For example, using pharmacogenomic data to customize medication selection has shown positive outcomes in pain management and mental health treatments.
Patient Involvement: Encouraging patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions strengthens their commitment to following treatment plans.
Cultural Sensitivity: Addressing cultural differences not only improves communication but also makes patients feel respected and understood, fostering stronger provider-patient relationships. You can consider providing multilingual resources and culturally sensitive materials, which studies show can reduce patient anxiety and improve adherence.
2. Improving Communication
Effective communication is essential to delivering a high-quality patient experience. Research also states clear, empathetic dialogue between patients and providers enhances understanding and promotes trust up to 63%.
Active Listening: When healthcare providers listen attentively to patients’ concerns, they can better tailor care approaches and ensure that patients feel valued and understood. Implementing reflective listening techniques helps confirm understanding and avoid miscommunication.
Avoiding Medical Jargon: Using plain language allows patients to better understand diagnoses, treatment options, and follow-up care instructions. Consider adopting “teach-back” methods where patients repeat information to confirm understanding.
Digital Communication Tools: Patient portals and messaging systems allow patients to communicate directly with their providers, view test results, and manage appointments. Automated messaging for appointment reminders and care plan follow-ups can improve adherence by 15%, according to recent studies.
3. Reducing Wait Times and Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Long wait times are a major source of patient dissatisfaction and can negatively impact care outcomes. Streamlining operations to reduce wait times significantly enhances the patient experience.
Advanced Scheduling Systems: Predictive analytics can improve appointment scheduling, helping clinics manage patient flow more effectively. By using patient check-in kiosks and automated scheduling tools, organizations can manage appointment peaks, reducing wait times.
Streamlining Clinical Workflows: Identifying and addressing bottlenecks in clinical workflows enables smoother patient transitions through different stages of care. Cross-training staff in multiple areas reduces delays caused by specific personnel shortages.
Training Staff for Efficiency: Well-prepared staff can manage patient flow proactively, minimizing delays and providing a smoother healthcare experience. Regular refresher courses on best practices in time management and workflow can reduce bottlenecks.
These operational enhancements help prevent delays in care, ensuring that patients receive timely attention and reducing the risk of abandoning or postponing necessary treatments.
4. Leveraging Technology
Integrating technology into healthcare services can dramatically improve the patient experience by enhancing accessibility, communication, and personalization.

Telehealth Services: Virtual care options expand access, especially for patients in remote or underserved areas. A study by the American Medical Association found telehealth use contributes to 80% of users reporting improved access to care.
Patient Portals: Secure portals allow patients to access their health records, view test results, and communicate with providers, increasing engagement and enabling self-management. Enabling test result alerts and medication reminders through portals has been shown to improve adherence and engagement.
AI-Driven Tools: Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing patient care by predicting needs, personalizing recommendations, and aiding in diagnostics. For example, AI algorithms can analyze patient data to identify early signs of complications, enabling preventive care.
Wearable Devices: Wearables provide real-time health data that patients and providers can use to monitor progress and adjust care plans accordingly. A report from Health IT Analytics shows that wearables reduce hospital readmission rates by up to 15%.
With these technological advances, healthcare organizations can offer patients greater convenience and control, leading to higher satisfaction and more efficient care.
5. The Role of Patient Feedback
Patient feedback is crucial for continuous improvement in healthcare delivery. When organizations actively seek and act on feedback, they demonstrate a commitment to quality and responsiveness. According to Press Ganey, healthcare organizations that prioritize patient feedback report a 10% increase in patient satisfaction.
Patient Satisfaction Surveys: Regular surveys provide insights into patient needs and highlight areas for improvement. Consider anonymous options to encourage honest feedback and a more accurate view of patient sentiment.
Focus Groups and Real-Time Feedback: Involving patients in focus groups or using digital feedback tools offers a deeper understanding of specific challenges. Real-time feedback kiosks within the facility allow patients to share concerns immediately, enabling quicker action.
Online Reviews and Social Media: Monitoring online feedback helps organizations gauge patient sentiment and address concerns proactively. Studies show that healthcare providers with high online ratings attract up to 40% more patients.
By choosing a statergy like personalized care, effective communication, operational efficiency, technology, and patient feedback, healthcare organizations can create a more patient-centered environment. These strategies not only enhance the patient journey but also build trust, reputation, and lasting patient relationships in a competitive healthcare landscape.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Many healthcare organizations are trying new and patient-focused ways to make care better, make patients happier, and improve overall results. Here, we look at several cases that show how these organizations have successfully integrated patient-centred practices and how their approaches can be used in various healthcare settings, from hospitals to outpatient clinics.
Case 1: Cleveland Clinic – Prioritizing Empathy and Communication
Cleveland Clinic has made empathy a part of its patient experience strategy. They developed the "Communicate with H.E.A.R.T." program, which trains staff across all roles to talk to patients. This initiative emphasizes active listening, clear explanations, and compassion in each patient interaction. Using this program helped patients feel happier and more confident with the staff.
Application Across Settings: You can use the same communication and empathy principles in different healthcare settings. In outpatient clinics, medical staff can make follow-up calls to check on patient progress, and hospitals might train all staff members to make sure each patient feels valued and understood.
Case 2: Kaiser Permanente – Streamlining Access to Care through Digital Tools
Kaiser Permanente launched an online portal and mobile app that gives patients access to their medical records, test results, and appointment scheduling. Patients can also use secure messaging to talk to their healthcare providers directly. These computer programs have made it easier for patients to get help and take control of their health care. Kaiser Permanente saw a 20% increase in patient satisfaction and a noticeable improvement in keeping appointments.
Application Across Settings:
Use online patient portals in both hospitals and outpatient settings. Smaller clinics might use telehealth platforms to accommodate patients with mobility challenges or those who live in remote areas. Larger hospitals might use them to centralize appointment and record management online.
Case 3: NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital – Reducing Fragmented Care through Multidisciplinary Teams
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital recognized the need to work together to address complex patient needs. This method helps doctors, nurses, and specialists talk to each patient and create a plan for their care. Patients at the hospital are happier because their treatment plans are clear and consistent, and the hospital has seen a 15% reduction in hospital readmissions.
Application Across Settings:
Multidisciplinary care teams are especially helpful in outpatient clinics that treat patients with complex needs, like diabetes or cardiovascular issues. In hospitals, this approach can include coordinating between departments to make sure patients move smoothly from in-patient care to out-patient care without the risk of information gaps.
Case 4: Mayo Clinic – Simplifying Administrative Processes for Patient Ease
Mayo Clinic has simplified administrative processes by digitizing patient registration, billing, and insurance claim processes. This has reduced the paperwork burden for patients. Mayo Clinic helps patients navigate insurance and billing issues more easily. This helps patients have a better patient experience overall. This approach reduced patient wait times for administrative tasks by 25% and improved patient satisfaction with administrative support by 30%.
Application Across Settings: Simplifying administrative processes benefits healthcare facilities of all sizes. For example, outpatient clinics can introduce electronic check-in kiosks to reduce wait times and streamline patient intake, while larger hospitals can adopt digital platforms that facilitate patient billing and insurance processing, minimizing stress and confusion.
Case 5: Johns Hopkins Medicine – Addressing Emotional Needs through Holistic Patient Support
Johns Hopkins Medicine uses emotional support programs in its patient care model to provide holistic healthcare. The hospital helps patients with emotional and mental support by offering counselling, support groups, and a team of patient advocates. This has made patients trust and stay loyal. Johns Hopkins reports that patients who used support services were 40% happier.
Application Across Settings: Emotional support is important in any healthcare setting. Smaller practices might offer counseling services or online support groups, while larger hospitals might have dedicated teams of social workers and mental health counselors who help patients feel emotionally supported throughout their care.
These case studies demonstrate the wide-ranging impact of patient-centred strategies across diverse healthcare environments. By prioritizing communication, digital access, care coordination, streamlined processes, and emotional support, healthcare organizations can significantly elevate patient experiences. Implementing these strategies helps improve patient satisfaction, outcomes, and operational efficiency, positioning healthcare providers to meet the growing demands for compassionate, accessible, and high-quality care.
Conclusion
A positive patient experience can improve clinical outcomes, strengthen patient loyalty, and raise institutional reputation. As healthcare becomes more competitive and patients expect smooth and kind care, it's important to give priority to patient experience. By making patient experience a part of their care delivery model, healthcare providers can improve patient satisfaction, improve outcomes, and build lasting patient relationships.
The strategies discussed in this article—ranging from personalized care approaches and technology integration to proactive engagement with patient feedback—offer practical steps for healthcare leaders committed to creating a patient-centered culture. These methods not only make healthcare providers more adaptable to patient needs but also distinguish them in an industry where responsiveness and empathy are critical to success.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, organizations that prioritize compassionate, patient-focused care will lead the way in redefining quality healthcare. By making patient experience a key focus, healthcare providers can ensure every interaction reflects their dedication to quality, respect, and the well-being of each patient.
Your Patients Deserve the Best. We Help You Hire Them! Attract and retain top healthcare talent with CWS Health’s strategic staffing solutions. Schedule a consultation today and take the first step toward a more efficient and compassionate workforce.
Nov 25, 2024
13 min read
Related Posts
Cogent Workforce Solutions Inc. © 2024. All Rights Reserved.
Services
Resources
Cogent Workforce Solutions Inc. © 2024. All Rights Reserved.
Quick Links
Resources
Services
-03.png)









.png)